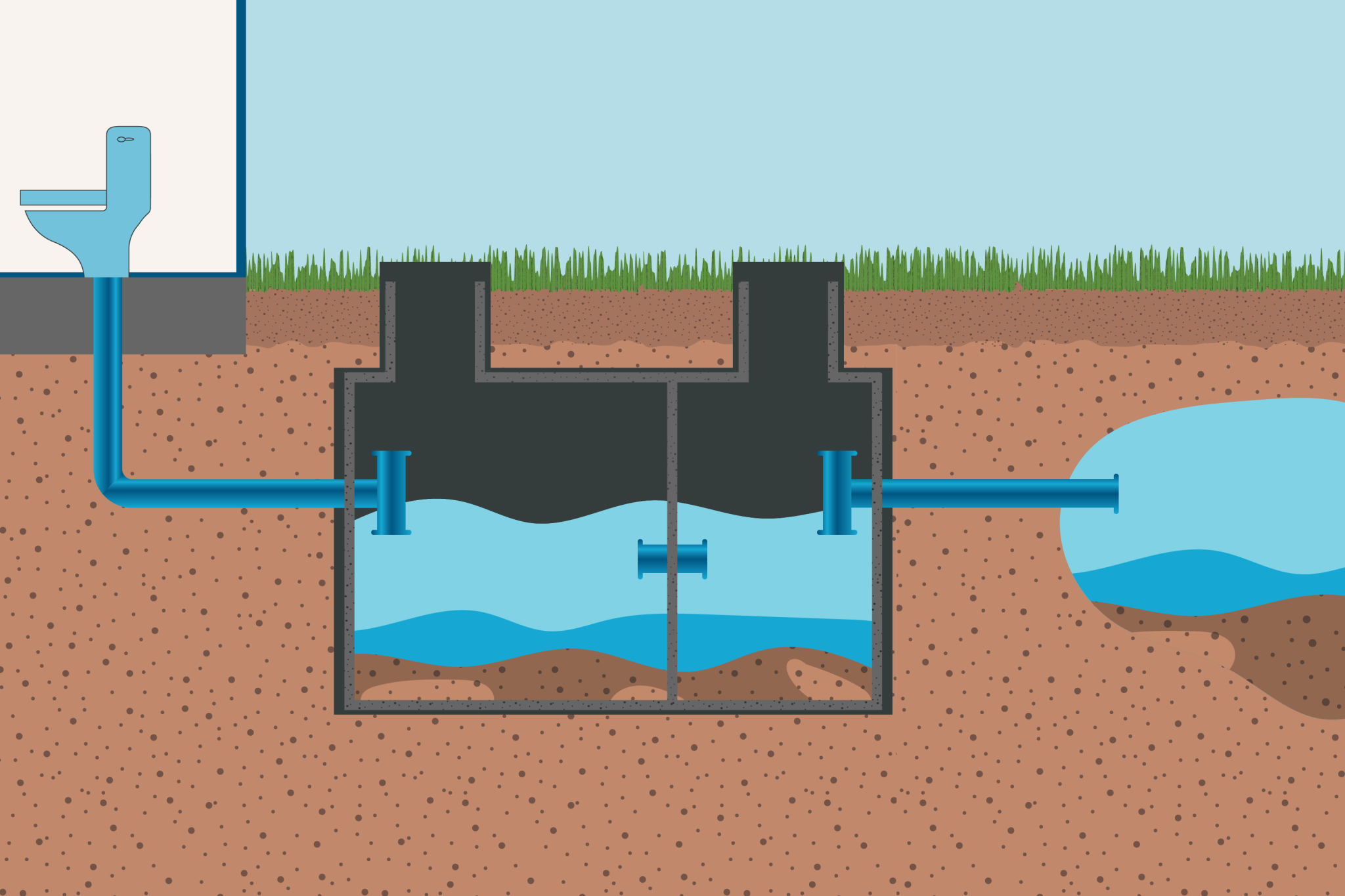
A properly installed septic system is crucial for safe wastewater management in off-grid homes, cabins, or tiny houses. This guide covers a conventional septic tank and drain field system that meets most health code requirements.
Before You Begin: Key Considerations
✔ Check local regulations (permits often required)
✔ Perform a percolation (“perc”) test to determine soil drainage
✔ Call 811 to locate underground utilities
✔ Choose location at least:
- 50+ feet from water sources
- 10+ feet from foundations
- 5+ feet from property lines
Materials Needed
- Septic tank (pre-cast concrete or plastic, typically 1,000-1,500 gal for 3-bedroom home)
- Perforated drain pipe (4″ diameter, PVC)
- Gravel (1½” to 2½” size, washed)
- Geotextile fabric
- PVC pipes and fittings
- Inspection pipes and risers
- Compactable fill dirt
- Excavation equipment (backhoe recommended)
Step 1: System Design
A. Size Your System
| Bedrooms | Tank Capacity (gal) | Drain Field Size (sq ft) |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | 750-900 | 300-450 |
| 3 | 1,000-1,200 | 600-900 |
| 4 | 1,250-1,500 | 900-1,200 |
B. Perc Test Results Determine Drain Field Size
| Perc Rate (min/inch) | Trench Length Needed |
|---|---|
| 1-5 | 30-50 ft per bedroom |
| 5-15 | 50-70 ft per bedroom |
| 15-30 | 70-100 ft per bedroom |
Step 2: Excavation
- Dig hole for septic tank (2′ wider than tank dimensions)
- Excavate trenches for drain field:
- 18-36″ wide
- 24-36″ deep
- Minimum 6′ apart
- Slope trenches 1/8″ to 1/4″ per foot for drainage
Step 3: Install Septic Tank
- Set tank in hole with inlet 4″ below house drain pipe elevation
- Connect inlet/outlet pipes using waterproof couplings
- Backfill around tank with native soil (no large rocks)
- Install risers for easy access (required in most areas)
Step 4: Build Drain Field
- Lay 6-12″ of gravel in trench bottoms
- Place perforated pipes (holes down) with 1/8″ slope
- Cover pipes with 2-6″ more gravel
- Wrap entire trench in geotextile fabric (prevents soil intrusion)
- Backfill with 12-18″ of native soil
Step 5: Connect House to System
- Run 4″ Schedule 40 PVC from house to tank:
- Maintain 1/4″ per foot slope
- Use long-radius elbows for turns
- Install cleanout every 50-75 feet
- Connect vent stack to house plumbing
Step 6: Final Grading & Vegetation
- Mound soil slightly over drain field to account for settling
- Plant grass only (no trees or deep-rooted plants)
- Mark tank and drain field locations for future reference
Maintenance Schedule
✅ Pump tank every 3-5 years ($200-$400)
✅ Inspect baffles and tees annually
✅ Never flush wipes, grease, or chemicals
✅ Divert rainwater away from drain field
Alternative Systems for Poor Soils
If your perc test fails:
- Mound System – Elevated drain field with sand fill
- Aerobic Treatment Unit – Mechanical aeration system
- Peat Filter System – Natural filtration medium
Cost Estimate
| Component | DIY Cost | Pro Installed |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000 gal tank | $800-$1,200 | $1,500-$2,500 |
| Drain field | $1,500-$3,000 | $3,000-$6,000 |
| Permits | $100-$500 | Included |
| Total | $2,500-$5,000 | $5,000-$10,000 |